Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Data Structures and Algorithms
1.1 Data structures
1.2 Introduction to Algorithms
1.3 Relation between data structures and algorithms
1.4 Abstract data types
1.5 Applications of ADTs
1.6 Algorithm efficiency
2. Searching and Algorithm Analysis
2.1 Searching and Algorithms
2.2 Binary search
2.3 Constant time operations
2.4 Growth of functions and complexity
2.5 O notation
2.6 Algorithm analysis
2.7 Recursive definitions
2.8 Recursive algorithms
2.9 Analyzing the time complexity of recursive algorithms
3. Sorting Algorithms
3.1 Sorting: Introduction
3.2 Selection sort
3.3 Insertion sort
3.4 Shell sort
3.5 Quicksort
3.6 Merge sort
3.7 Radix sort
3.8 Overview of fast sorting algorithms
3.9 Python: Sorting with different operators
4. Lists
4.1 List abstract data type (ADT)
4.2 Singly-linked lists
4.3 Singly-linked lists: Search and insert
4.4 Singly-linked lists: Remove
4.5 Doubly-linked lists
4.6 Doubly-linked lists: Search and insert
4.7 Doubly-linked lists: Remove
4.8 Linked list traversal
4.9 Sorting linked lists
4.10 Linked list dummy nodes
4.11 Linked lists: Recursion
4.12 Array-based lists
5. Stacks and Queues
5.1 Stack abstract data type (ADT)
5.2 Stacks using linked lists
5.3 Array-based stacks
5.4 Queue abstract data type (ADT)
5.5 Queues using linked lists
5.6 Array-based queues
5.7 Deque abstract data type (ADT)
5.8 Using a Python list as a stack
5.9 Python queue class
6. Hash Tables
6.1 Map ADT
6.2 Hash tables
6.3 Chaining
6.4 Linear probing
6.5 Quadratic probing
6.6 Double hashing
6.7 Hash table resizing
6.8 Common hash functions
6.9 Direct hashing
6.10 Hashing Algorithms: Cryptography, Password Hashing
6.11 Python dictionary
7. Trees
7.1 Binary trees
7.2 Applications of trees
7.3 Binary search trees
7.4 BST: Search algorithm
7.5 BST: Insertion
7.6 BST: Removal
7.7 BST: Traversal
7.8 BST: Height and insertion order
7.9 BST: Recursion
7.10 BST: Parent node references
7.11 Set abstract data type (ADT)
7.12 Implementing a set ADT with a BST
7.13 Python set class
7.14 Tries
8. Balanced Trees
8.1 AVL: A balanced tree
8.2 AVL rotations
8.3 AVL insertions
8.4 AVL removals
8.5 Red-black tree: A balanced tree
8.6 Red-black tree: Rotations
8.7 Red-black tree: Insertion
8.8 Red-black tree: Removal
9. Heaps and Treaps
9.1 Heaps
9.2 Heaps using arrays
9.3 Heapsort
9.4 Priority queue abstract data type (ADT)
9.5 Treaps
9.6 Python PriorityQueue class
10. Graphs
10.1 Graphs: Introduction
10.2 Applications of graphs
10.3 Graph representations: Adjacency lists
10.4 Graph representations: Adjacency matrices
10.5 Directed graphs
10.6 Weighted graphs
10.7 Vertex, Edge, and Graph classes
10.8 Graphs: Breadth-first search
10.9 Graphs: Depth-first search
10.10 Algorithm: Dijkstra’s shortest path
10.11 Algorithm: Bellman-Ford’s shortest path
10.12 Topological sort
10.13 Minimum spanning tree
10.14 All pairs shortest path
11. Algorithms
11.1 Huffman compression
11.2 Huffman compression: Implementation
11.3 Heuristics
11.4 Greedy algorithms
11.5 Dynamic programming
12. B-trees
12.1 B-trees
12.2 2-3-4 tree: Search
12.3 2-3-4 tree: Insertion
12.4 2-3-4 tree: Rotation and fusion
12.5 2-3-4 tree: Removal
13. Additional Material
13.1 Bubble sort
13.2 Quickselect
13.3 Bucket sort
13.4 Circular lists
Teach Data Structures in Python with this hands-on, interactive zyBook with customizable zyLabs
Data Structures in Python is suitable for a first course in data structures and algorithms, especially common in the first two years of a computing major.
- Introduces the basics of algorithms and data structures, including sorting, runtime complexity, lists, stacks, queues, hash tables, trees, and graphs
- Packed with over 1,000 learning questions and animations to help students master the material
- Python implementations of many data structures and algorithms are available throughout the book
- Adopters have access to a test bank with questions for every chapter
See how content is covered:
What is a zyBook?
Data Structures in Python is a web-native, interactive zyBook that helps students visualize concepts to learn faster and more effectively than with a traditional textbook. Check out our research.
Since 2012, over 1,800 academic institutions have adopted digital zyBooks to transform their STEM education.
zyBooks benefit both students and instructors:
- Instructor benefits
- Customize your course by reorganizing existing content, or adding your own content
- Continuous publication model updates your course with the latest content and technologies
- Robust reporting gives you insight into students’ progress, reading and participation
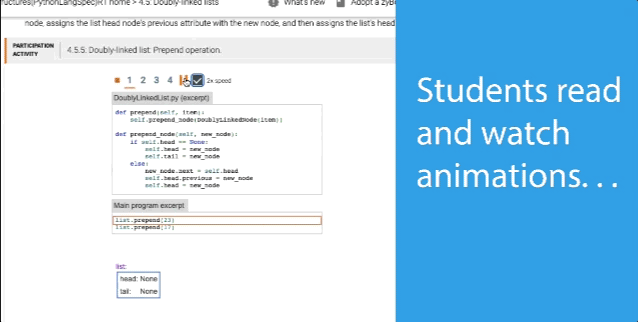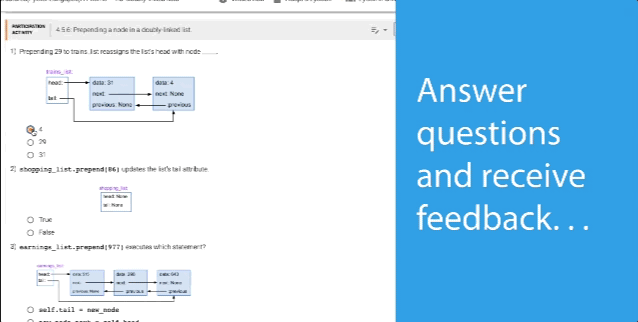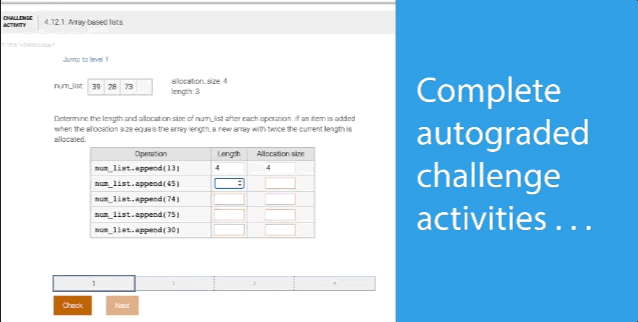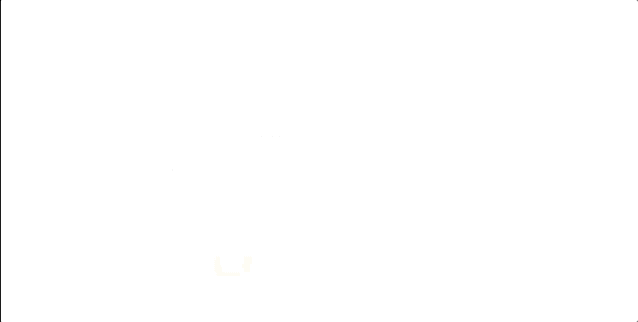
- Save time with auto-graded labs and challenge activities that seamlessly integrate with your LMS gradebook
- Build quizzes and exams with hundreds of included test questions
- Student benefits
- Learning questions and other content serve as an interactive form of reading
- Instant feedback on labs and homework
- Concepts come to life through extensive animations embedded into the interactive content
- Review learning content before exams with different questions and challenge activities
- Save chapters as PDFs to reference the material at any time
What is a zyLab?
See the capabilities of the zyBooks programming environment
Author
Evan Olds
Senior Content Developer, zyBooks
Roman Lysecky
Professor Emeritus of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Univ. of Arizona